Capacitor, Resistor, Inductor
Gravity Arduino Analog Turbidity Sensor In Pakistan
Condition: New
Availability:
In Stock
Advance Payment Only
SKU: B 283,IMP10,Th2,KRT
Rs.2400
Rs. 3000
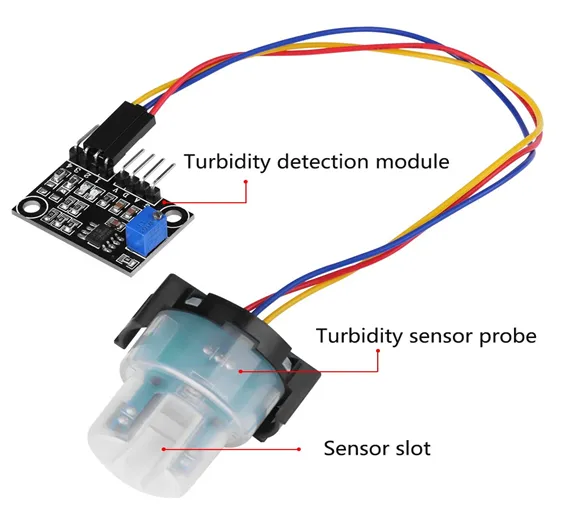
The
gravity
arduino
turbidity
sensor
detects
water
quality
by
measuring
the
levels
of
turbidity.
It
uses
light
to
detect
suspended
particles
in
water
by
measuring
the
light
transmittance
and
scattering
rate,
which
changes
with
the
amount
of
total
suspended
solids
(TSS)
in
water.
As
the
TTS
increases,
the
liquid
turbidity
level
increases.
Turbidity
sensors
are
used
to
measure
water
quality
in
rivers
and
streams,
wastewater
and
effluent
measurements,
control
instrumentation
for
settling
ponds,
sediment
transport
research
and
laboratory
measurements.
This
liquid
sensor
provides
analog
and
digital
signal
output
modes.
The
threshold
is
adjustable
when
in
digital
signal
mode.
You
can
select
the
mode
according
to
your
MCU.
mb-3'>Specifications: Operating
Voltage:
5V
DC Operating
Current:
40mA
(MAX) Response
Time
:
<500ms Insulation
Resistance:
100M
(Min) Analog
output:
0-4.5V Digital
Output:
High/Low
level
signal
(you
can
adjust
the
threshold
value
by
adjusting
the
potentiometer) Operating
Temperature:
5℃~90℃ Storage
Temperature:
-10℃~90℃ Weight:
30g Adapter
Dimensions:
38mm*28mm*10mm/1.5inches
*1.1inches*0.4inches
mb-3'>Interface
Description: "D/A"
Output
Signal
Switch "A":
Analog
Signal
Output,
the
output
value
will
decrease
when
in
liquids
with
a
high
turbidity "D":
Digital
Signal
Output,
high
and
low
levels,
which
can
be
adjusted
by
the
threshold
potentiometer Threshold
Potentiometer:
you
can
change
the
trigger
condition
by
adjusting
the
threshold
potentiometer
in
digital
signal
mode.
mb-3'>Examples:
Here
are
two
examples:
mb-3'>Example
1
uses
Analog
output
mode
Example
2
uses
Digital
output
mode
mb-3'>Example
1
void
setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
//Baud
rate:
9600 } void
loop()
{
int
sensorValue
=
analogRead(A0);//
read
the
input
on
analog
pin
0:
float
voltage
=
sensorValue
*
(5.0
/
1024.0);
//
Convert
the
analog
reading
(which
goes
from
0
-
1023)
to
a
voltage
(0
-
5V):
Serial.println(voltage);
//
out
the
value
you
read:
delay(500); }
Example
2
int
ledPin
=
13;
//
Connect
an
LED
on
pin
13,
or
use
the
onboard
one int
sensor_in
=
2;
//
Connect
turbidity
sensor
to
Digital
Pin
2
void
setup(){
pinMode(ledPin,
OUTPUT);
//
Set
ledPin
to
output
mode
pinMode(sensor_in,
INPUT);
//Set
the
turbidity
sensor
pin
to
input
mode }
void
loop(){
if(digitalRead(sensor_in)==LOW){
//read
sensor
signal
digitalWrite(ledPin,
HIGH);
//
if
sensor
is
LOW,
then
turn
on
}else{
digitalWrite(ledPin,
LOW);
//
if
sensor
is
HIGH,
then
turn
off
the
led
} }
This
is
a
reference
chart
for
the
mapping
from
the
output
voltage
to
the
NTU
according
to
different
temperature.
e.g.
If
you
leave
the
sensor
in
the
pure
water,
that
is
NTU
<
0.5,
it
should
output
“4.1±0.3V”
when
temperature
is
10~50℃.
characteristic




